A payroll journal entry is an accounting record that reflects the payroll expenses and related liabilities for a given accounting period.
What is Payroll Journal Entry?
A payroll journal entry is an accounting record that reflects the payroll expenses and related liabilities for a given accounting period. It is used to record the expenses associated with paying employees and the corresponding liabilities for taxes and other withholdings. The journal entry ensures that the payroll expenses are accurately reflected in the company’s financial statements.
Components of a Payroll Journal Entry
- Gross Wages:
- Represents the total amount of wages earned by employees before any deductions.
- Deductions:
- Employee Deductions: Taxes and other withholdings from employees’ paychecks, such as income tax, Social Security tax, Medicare tax, retirement contributions, and insurance premiums.
- Employer Contributions: The employer’s share of payroll taxes, such as Social Security and Medicare taxes, which are not deducted from employee wages.
- Net Pay:
- The amount that employees actually receive after all deductions have been made.
- Liabilities:
- Amounts owed to third parties, such as tax authorities or benefit providers, related to payroll deductions.
Example Payroll Journal Entry
Assume a company has the following payroll for a pay period:
- Gross Wages: $10,000
- Employee Deductions:
- Federal Income Tax Withheld: $1,200
- Social Security Tax Withheld: $620
- Medicare Tax Withheld: $145
- Health Insurance Premiums Withheld: $200
- Employer Contributions:
- Social Security Tax: $620
- Medicare Tax: $145
Net Pay:
- Net Pay to Employees: $10,000 – ($1,200 + $620 + $145 + $200) = $7,835
Here’s how the journal entry might look:
- Record Payroll Expense:
- Debit Salaries and Wages Expense: $10,000
- This represents the total expense of employee wages.
- Debit Salaries and Wages Expense: $10,000
- Record Employee Deductions:
- Credit Federal Income Tax Payable: $1,200
- Credit Social Security Tax Payable: $620
- Credit Medicare Tax Payable: $145
- Credit Health Insurance Payable: $200
- These credits represent liabilities for amounts withheld from employees’ wages.
- Record Employer Payroll Taxes:
- Credit Social Security Tax Payable: $620
- Credit Medicare Tax Payable: $145
- These credits reflect the employer’s contribution to Social Security and Medicare taxes.
- Record Payment to Employees:
- Credit Cash/Bank Account: $7,835
- This reflects the cash paid out to employees as net pay.
- Credit Cash/Bank Account: $7,835
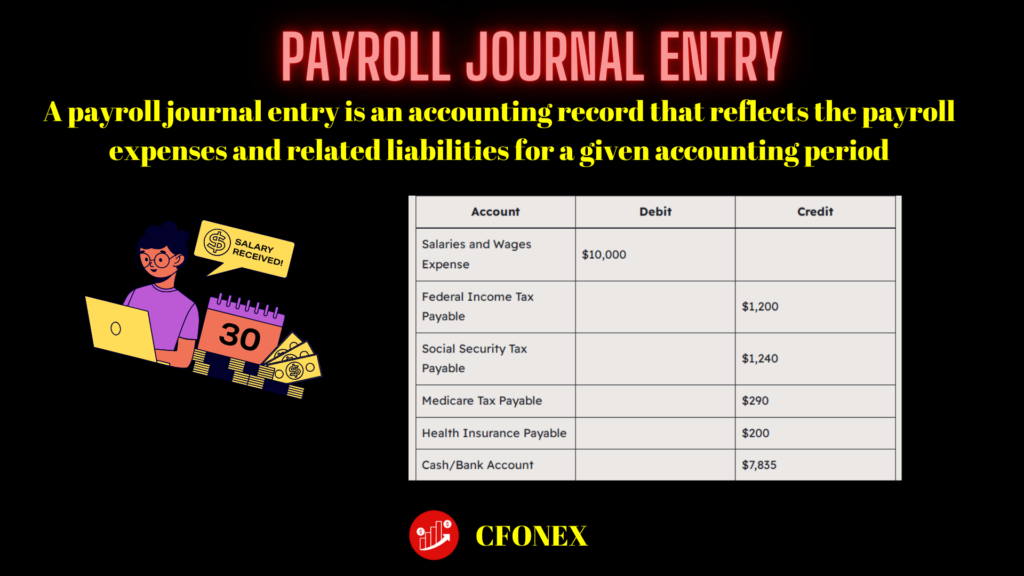
Payroll Journal Entry Example:
| Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Salaries and Wages Expense | $10,000 | |
| Federal Income Tax Payable | $1,200 | |
| Social Security Tax Payable | $1,240 | |
| Medicare Tax Payable | $290 | |
| Health Insurance Payable | $200 | |
| Cash/Bank Account | $7,835 |
Key Points
- Accuracy: Ensure that all calculations are correct, including gross wages, deductions, and employer contributions.
- Consistency: Regularly update the journal entries to reflect each payroll period and any changes in tax rates or benefit plans.
- Documentation: Maintain supporting documentation for all payroll entries, including timesheets, payroll reports, and tax filings.
In summary, a payroll journal entry records all payroll-related expenses and liabilities, including gross wages, deductions, employer contributions, and net pay. It ensures accurate financial reporting and compliance with accounting principles.
Leave a Reply