Accounting equation, also called balance sheet equation, is the foundation of double-entry accounting system that states total assets are equal to the sum of total liabilities and equity.
Definition, Components, Examples
Accounting Equation Definition
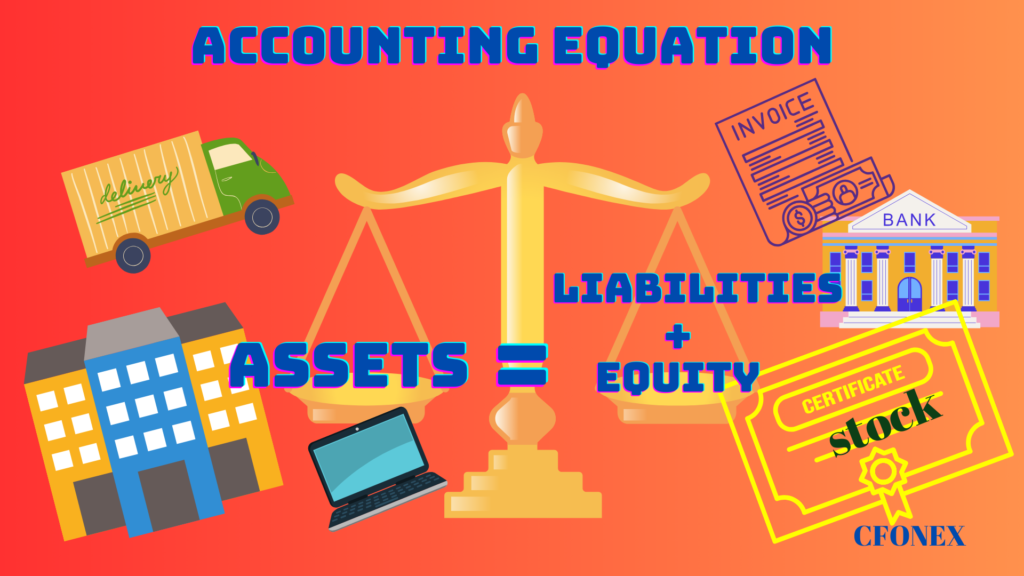
The accounting equation, also known as balance sheet equation, shows the relationship between assets, liabilities, and equity.
Accounting equation is the foundation of double-entry accounting system and a basic principle of accounting that states a company’s total assets are equal to the sum of all total liabilities and equity.

Based on the accounting equation, the total dollar amounts of the two sides are always equal. For example, an increase in an asset account can be matched by an equal increase to a related liability or equity account.
Every transaction affects at least two accounts in a way that keeps the accounting equation in balance.
Accounting Equation Components
The accounting equation is made up of three main components and they are: Assets, liabilities, and Equity.
A company owns assets that may be partially owned by owners (stockholders) and/or partially owned by outsiders (debtors).
Whenever a company purchases an asset, there are two ways to pay for it: either it pays for the asset with equity (its own money) or through liability (other people money)

- Assets (what it owns): Assets are any item of value or resources that a company owns or controls such as cash, accounts receivable, inventory, prepaid insurance, investments, land, buildings, equipment, and goodwill.
- Liabilities (what it owes to others): Liabilities are debts or obligations that a company owes to others such as accounts payable, notes payable, salaries and wages payable, interest payable, and income tax payable.
- Equity (the difference between assets and liabilities): Represents the residual interest or the leftover when a company sells all its assets and pays the liabilities. How much owners have invested into the company along with any retained profit or losses.
Expanded Accounting Equation
The basic format for the accounting equation is:
Assests = Liabilities + Equity
Accounting Equation Examples
Examples of accounting equation:
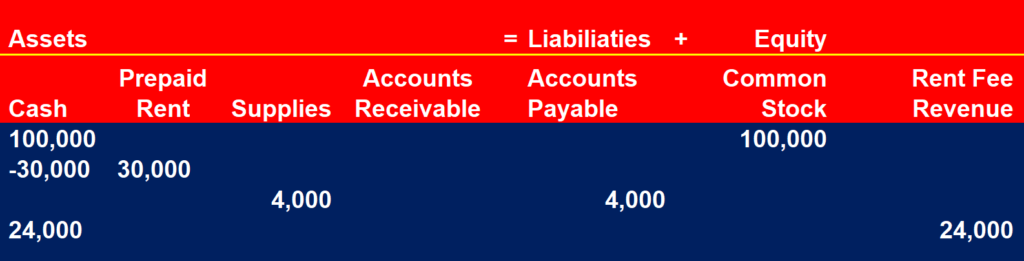
Palm Coast started a company to provide assisted living housing for seniors. Shareholders invested $100,000 in the company:

Palm Coast signed a one-year for the housing. The lease requires the company to pay for the whole year to get more discount. Palm Coast paid $30,000 for the whole year rent.

Palm Coast bought supplies on account for the facility in the amount of $4,000.

Palm Coast received made 24,000 in rent fees for the current month from residents. Each room is leased for $2,000 for 12 residents.
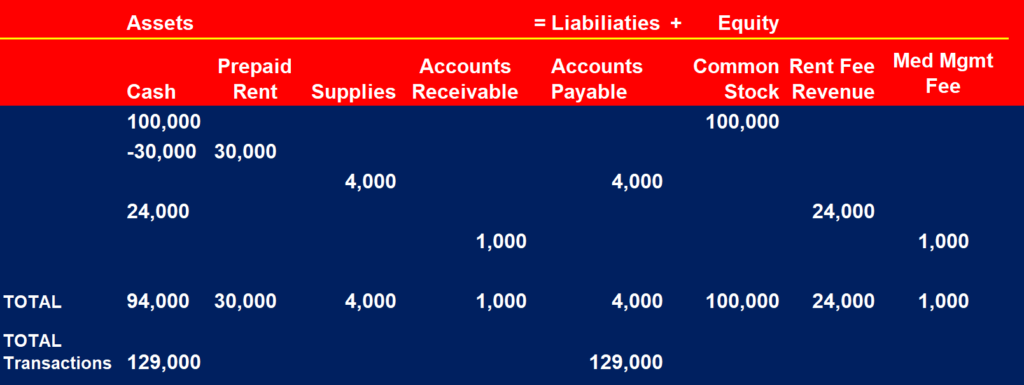
Palm Coast receive provided medical management for 4 residents in the amount of $1,000. The med management fees will be paid next month when residents receive bill.

Here is the total for all transactions. As we see, total assets equal total liabilities and equities.
Leave a Reply